

10 Ways Space Exploration Benefits Earth Part I
When we think about space exploration, it’s not uncommon to imagine glorious spectacles of blue-marbled Earth or orange-glowing galaxies stationed billions of lightyears away. We think of the vast expense of endless stars but rarely consider how it impacts our lives here on Earth.
As humanity works to discover what lies far beyond Earth’s orbit, we synergistically improve the lives of the beings existing beneath it. As we launched the first satellites into space, to first get our sea legs in the ether, that knowledge and capability enabled the GPS constellation, accurate weather forecasting and modern telecommunications. Three technologies our modern day civilization could not live without.
Space exploration has played a crucial role in the innovation and advancement of humanity for decades. Still, as technology (and let’s face it, billionaire funding) continues to evolve, the benefits of investing in space exploration have never been more apparent. Let’s look at how space exploration benefits our home planet.
1. Advanced Robotics and AI
Space, and everything outside of Earth’s atmosphere, is a harsh environment. Robots and AI are our mechanisms of exploration, and the best minds are always at work developing the technology that allows us to roam the surface of Mars and beyond. Those same technologies trickle down to be used on the third planet as well, from supporting mobility for disabled persons to aiding in search and rescue efforts.
2. Safer Food
The challenge of providing safe, contaminant-free food for astronauts was a vast undertaking that led to some pretty unconventional methods (space ice cream just doesn’t hit quite the same). The Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Point concept that Pillsbury developed for NASA to eliminate microorganism contamination aboard spacecraft is now used by the FDA to ensure the safety of store-bought foods.
3. Cleaner Water
One of the most significant contributions space exploration has given planet Earth comes in liquid form. The need to properly filter water for space travelers prompted NASA to develop a way to filter water in a simple, portable manner efficiently. As a result, inexpensive, easy-to-use water filtration systems were designed and used worldwide to provide clean drinking water or grow crops in otherwise barren soil.
4. Asteroid Aversion
Earth-bound asteroids are nothing to scoff at; ask any prehistoric creature. The truth is, the collision of Earth with any meteor any larger than 100 meters across would cause an apocalyptic disaster. Attentive space presence and the actual existing technology of spacecraft-driven nuclear explosions could be enough to keep humankind from experiencing the same fate as our mammoth predecessors.
5. Medical Innovation
Aboard the International Space Station, astronauts have been able to experiment with and finetune medical innovations that have transformed healthcare on Earth. From life-saving cancer treatments to delicate robotic surgery performed inside an MRI machine, the future of advanced medicine is happening in conjunction with space exploration.
6. Sourcing of Critical Raw Materials
We already know that meteorites deliver rare, often unheard of metals and elements to Earth or leave dustings of gold across their paths. But other rare earth elements can be found as close by as the moon. Helium-3, for example, is used for some specific MRIs and is a potential fuel for nuclear power plants. Like europium and tantalum, other elements are used in advanced electronics and solar panels.
7. Combating Climate Change
One of the primary challenges of space travel is the removal of carbon dioxide from the air in space stations and planetary outposts. As powerful brains get to work on cleaning the air aboard spacecraft, we’re learning more about how we could potentially reduce the presence of the same damaging compound in our environment. Additionally, satellites that circle our home planet can provide precise data that helps us understand and moderate climate change.
8. World Peace
The International Space Station has hosted astronauts and spacecraft from eighteen countries during its time in orbit. Space exploration may be the key to international cooperation, forging greater trust and stronger diplomatic relationships between otherwise distant countries. Just recently, this international cooperation has been strained due to the conflict in Ukraine, but so far those ties have bent, not broken and there are reasons to be hopeful that the international partnership will continue to endure and inspire.
9. Nurturing Human Curiosity
Human beings are naturally curious creatures, and our desire to explore and learn sets us apart from other life on Earth. Space exploration paints an insightful picture of our small place in the universe and gives us a glimpse of inexplicable magic. With each new galaxy discovered and every black hole detected, our human curiosity is satisfied and propelled and keeps us asking, Is there another life out there in the universe?
10. Inspiring Future Generations
As the youngest person to ever fly to space joined a SpaceX mission, kids worldwide suddenly saw an impossible dream become a reality. Space travel is no longer pure science fiction or just for the lucky few. For the first time in human history, children can see the possibility of experiencing space, encouraging science education and careers that will build a global capacity for astonishing innovation.
While space exploration is largely about discovering the unknown frontier, its pursuit has proven beneficial for so many facets of our life here on Terra Firma. In fact, those glowing rockets jetting into the atmosphere have a greater impact on our daily lives than many of us realize.

Share This Story, Choose Your Platform!
Related posts.


10 Benefits of Space Exploration. (Including Medical and Economical)
On April 12, 1961, the Russian cosmonaut Yuri Gagarin became the first human to journey to outer space. The age of space exploration started that day.
But why are we so interested in spending so much time, money, and resources to visit chunks of rock that are most likely empty? Why purposely go to environments that are dangerous and even deadly to humans?
Well, the answer is simple.
The benefits of space exploration outweigh the dangers of it. Becoming a space-faring civilization is the most important goal we must achieve for humanity to survive long-term .
In this article, we’ll the major 10 benefits of space exploration. These include medical, technological, and economic benefits. They are listed in no particular order of importance.
Economic benefits of space exploration

10. Creation of STEM Jobs
NASA employs more than 18,000 people. SpaceX more than 12,000. And that’s not counting outside contractors with whom those numbers at least double.
A lot of those jobs are positions for engineers, data analysts, mathematicians, physicists, astronomers, doctors, biologists, geologists, etc.
Space exploration is one of the industries that require the largest percentage of STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) jobs.
These positions require highly qualified people to fill them but are also some of the highest-paid jobs in the market. The average entry-level STEM job pays approximately 26% higher than non-STEM fields for college graduates.
So, in summary, the growing space industry creates high-paying jobs.
9. Space mining and asteroid capturing
In space, there are many valuable resources in big quantities that are scarce on Earth. For example, the asteroid Pysche 16 is estimated to contain over $700 quintillion dollars worth of gold. Enough to give each person on Earth more than $100 billion dollars. And that’s not even close to being the most valuable object.
Economists have predicted the space mining industry will create the first trillionaire.
But the real benefit for the advancement of humankind might come from a much more unlikely substance. Water.
Learning to capture asteroids full of ice and crashing them safely, could help us solve one of the biggest challenges of inhabiting planets. The lack of liquid water.
8. Space tourism industry
The biggest dream some of us have is being able to take a trip to outer space. It is the ultimate destination. And because unfortunately, not many people can become astronauts, the rest of us will have to wait until the space tourism industry develops a bit more. It is still too expensive to go to space .
In 2021, a trip in one of the first trips offered by Blue Origin, the space company created by Jeff Bezos, was auctioned. The winner paid $28 million for the privilege to be one of the first space tourists.
As reusable rockets improve, the costs of these trips will become significantly lower. Hopefully one day they’ll be within the reach for all of us.
The space tourism industry will indubitably create tens of thousands of jobs. From travel agents to pilots, to manufacturing jobs in the factories that make the rockets.
Medical benefits of space exploration

7. Learning more about the human body
Studying the effects of space travel has helped us better understand the human body. For example, analyzing the effects of zero-gravity on blood circulation led to many discoveries on how arteries age and how to prevent some types of heart failure.
The experiments and measurements of bone strength and bone loss in astronauts have helped doctors better understand osteoporosis and other bone diseases.
The medical benefits of space exploration extend to pretty much every area of the human body. From muscle physiology to mental health.
6. Improving medical assistance in remote areas
One of the biggest challenges of space travel is solving problems when you can’t send any new equipment, experts, or any other help. You have to fix things with whatever is available on the ship.
So what happens when there’s a medical emergency on a spaceship?
This question has led doctors and engineers to develop tools and machines that can perform medical procedures and diagnostics remotely.
That same technology has many applications on Earth too. It allows doctors to assist patients that are located in remote rural areas or villages that are difficult to access.
5. Development of new medical procedures
All this knowledge that has been collected has yielded many developments in medical procedures.
Some examples of medical advancements that have been created thanks to space exploration are:
- Heart pumps
- Programmable pacemakers
- Fiber-optic catheters to perform laser angioplasty
- Digital imaging breast biopsy used to detect breast cancer
- Fetus monitoring transmitters
- Cooling suits made to lower a person’s temperature
The NASA spinoff site keeps track of some of the health and medicine advancements that have been made possible thanks to space exploration.
Other benefits of space exploration
4. development of new technologies.
The space race is one of the eras that has birthed the most technological advancements in the shortest period of time. It is probably only third behind both world wars. Throughout the years, companies have found consumer uses for many of these developments. To this day we still use them in our day-to-day lives without even knowing that some NASA engineers originally developed them for the Apollo program that took humankind to the Moon.
Listing all the technologies that have been derived from space exploration would be impossible, but here are some notable examples.
- Vacuum sealed food.
- Shock-absorbing sneaker soles. That’s right, the comfy running soles were originally developed for astronaut spacesuits.
- Fireproof materials used in firefighter uniforms
- Quake-proofing technology used in bridges and buildings to resist Earthquakes
- Heat-repellent blankets. There’s a reason why they are also known as “space blankets”. Fun fact, they can also double as DIY telescope covers.
- Rechargeable hearing aids
- Autonomous drone navigation
- Modern vacuum cleaners
- The lenses used in “action cameras”
- Water purification technology
As you can see, it is important for us to keep pushing the limits of space exploration. Who knows what kind of new technologies could be developed that will make our lives easier in the future.
3. Inspire the next generation
Space exploration sparks the curiosity of children who will become the next Elon Musk, Neil Armstrong, Sally Ride, or Guion Bluford.
It inspires students to dream and gets them interested in science and technology.
Not only is this good for them as STEM jobs can secure them a comfortably future, but it also helps humanity. It is through invention, research, and knowledge that humanity will be able to overcome the big challenges it will be facing in the future.
2. Protecting Earth
We only have one planet where we can live without the help of spacesuits. It would be nice to keep it in good condition until we can figure out a way to find other habitable planets or terraform others.
To do that, we need to learn more about the dangers of space. We know about extinction events like asteroids, but that’s not the only potential threat to our survival. Solar flares, radiation, magnetic pole changes, and greenhouse effects are just some of the challenges Earth might face at some point.
Exploring space is the only way we will learn more about them so we can develop strategies and technology that could help save us from such events.
1. Increase humanity’s odds of survival
There’s one thing we are certain of about when it comes to space. If we – humanity – don’t become a space-faring civilization. We will become extinct sooner or later.
Earth will eventually become uninhabitable and will probably be devoured by the Sun as it expands during the later years of its life cycle. And that’s hoping nothing else happens before, like an asteroid impact, an ice age, atmospheric loss, climate change, or any other potential threats that could wipe us out, to put it bluntly.
Space exploration is not a luxury for the richest nations. It should be a worldwide priority and every country needs to come together in this effort. It is simply the only way we can hope to survive as a species.
We don’t know if we have millions of years or hundreds of years before any of these events happen. So it’s better to get started today.
- Space exploration can be the doorway to many growth industries such as asteroid mining or space tourism.
- Many medical advancements have been made possible thanks to the aerospace industry.
- Space exploration is critical and the only path to the survival of the human race.
Elena is a Canadian journalist and researcher. She has been looking at the sky for years and hopes to introduce more people to the wonderful hobby that is astronomy.
Related Posts

What Happened to the Mars Helicopter? (Ingenuity)

What is the Purpose of the International Space Station?

Who Owns The International Space Station?

Is There Gold On The Moon? Yes! And Here’s Why It Matters.

Is There Gold On Mars? Yes! And The Discovery Was Very Curious…
Have We Landed On Venus?
- Buying Guides
- Telescope Accessories
- Magnification Calculator
- Field of View Calculator
- Constellations
- Solar System
- Space Exploration
- Name All The Planets
- Name All 88 Constellations
- Name The 12 Zodiac Constellations
- Name All The Moons
Type above and press Enter to search. Press Esc to cancel.

Suggested Searches
- Climate Change
- Expedition 64
- Mars perseverance
- SpaceX Crew-2
- International Space Station
- View All Topics A-Z
- Humans in Space
Earth & Climate
The solar system, the universe, aeronautics, learning resources, news & events.

NASA’s Webb Reveals Smallest Asteroids Yet Found in Main Asteroid Belt

Avalanches, Icy Explosions, and Dunes: NASA Is Tracking New Year on Mars

What’s Up: December 2024 Skywatching Tips from NASA
- Search All NASA Missions
- A to Z List of Missions
- Upcoming Launches and Landings
- Spaceships and Rockets
- Communicating with Missions
- James Webb Space Telescope
- Hubble Space Telescope
- Why Go to Space
- Commercial Space
- Destinations
- Living in Space
- Explore Earth Science
- Earth, Our Planet
- Earth Science in Action
- Earth Multimedia
- Earth Science Researchers
- Pluto & Dwarf Planets
- Asteroids, Comets & Meteors
- The Kuiper Belt
- The Oort Cloud
- Skywatching
- The Search for Life in the Universe
- Black Holes
- The Big Bang
- Dark Energy & Dark Matter
- Earth Science
- Planetary Science
- Astrophysics & Space Science
- The Sun & Heliophysics
- Biological & Physical Sciences
- Lunar Science
- Citizen Science
- Astromaterials
- Aeronautics Research
- Human Space Travel Research
- Science in the Air
- NASA Aircraft
- Flight Innovation
- Supersonic Flight
- Air Traffic Solutions
- Green Aviation Tech
- Drones & You
- Technology Transfer & Spinoffs
- Space Travel Technology
- Technology Living in Space
- Manufacturing and Materials
- Science Instruments
- For Kids and Students
- For Educators
- For Colleges and Universities
- For Professionals
- Science for Everyone
- Requests for Exhibits, Artifacts, or Speakers
- STEM Engagement at NASA
- NASA's Impacts
- Centers and Facilities
- Directorates
- Organizations
- People of NASA
- Internships
- Our History
- Doing Business with NASA
- Get Involved
NASA en Español
- Aeronáutica
- Ciencias Terrestres
- Sistema Solar
- All NASA News
- Video Series on NASA+
- Newsletters
- Social Media
- Media Resources
- Upcoming Launches & Landings
- Virtual Guest Program
- Image of the Day
- Sounds and Ringtones
- Interactives
- STEM Multimedia

Lab Work Digs Into Gullies Seen on Giant Asteroid Vesta by NASA’s Dawn

Hubble Spies a Cosmic Eye

Station Science Top News: Dec. 20, 2024

Artemis II Core Stage Vertical Integration Begins at NASA Kennedy
NASA, Axiom Space Change Assembly Order of Commercial Space Station

Cutting-Edge Satellite Tracks Lake Water Levels in Ohio River Basin

NASA-DOD Study: Saltwater to Widely Taint Coastal Groundwater by 2100

NASA Study: Crops, Forests Responding to Changing Rainfall Patterns

NASA Finds ‘Sideways’ Black Hole Using Legacy Data, New Techniques

NASA Open Science Reveals Sounds of Space

F.5 FINESST: SMD’s Graduate Student Research Clarifications and Corrections

ROSES-24 A.62 FarmFlux Science Team Updates


Amendment 88: A.52 Advanced Component Technology Text and Due Dates Released

2024: NASA Armstrong Prepares for Future Innovative Research Efforts

NASA, Notre Dame Connect Students to Inspire STEM Careers

NASA Flight Rerouting Tool Curbs Delays, Emissions

NASA’s New Deep Space Network Antenna Has Its Crowning Moment

NASA Partners with US Patent and Trademark Office to Advance Technology Transfer

They Grow So Fast: Moon Tree Progress Since NASA’s Artemis I Mission
Five Ways to Explore NASA’s Portfolio of Technologies with TechPort 4.0

25 Years Ago: STS-103, The Hubble Servicing Mission-3A

La NASA identifica causa de pérdida de material del escudo térmico de Orion de Artemis I

Preguntas frecuentes: La verdadera historia del cuidado de la salud de los astronautas en el espacio

El X-59 enciende su motor por primera vez rumbo al despegue
Human spaceflight technologies benefitting earth.
Erin Mahoney
New power sources, fission surface power, advanced solar arrays, additive manufacturing, 3d-printed habitats, laserjet solar cells, cleaner air, water, food, environmental control and life support systems, pollution detection, space canary, mpass – aerosol sensor, there’s more space in your life than you think.
Space exploration and its relationship with Earth is symbiotic. Often, what works for one benefits the other, and vice versa. This Earth Day, as NASA prepares to send humans farther into the solar system than ever before, the agency is advancing its understanding of fundamental sciences on the International Space Station and working on technologies for Artemis that will benefit future space exploration and life here on Earth. This ambitious exploration endeavor requires new technologies and global innovation to ensure our astronauts can safely and effectively conduct ground-breaking research today aboard the space station, soon at the Moon, and then at Mars. Many of those technologies developed to send our explorers deeper into space for longer periods of time can also come back to Earth for the benefit of humanity and the environment.
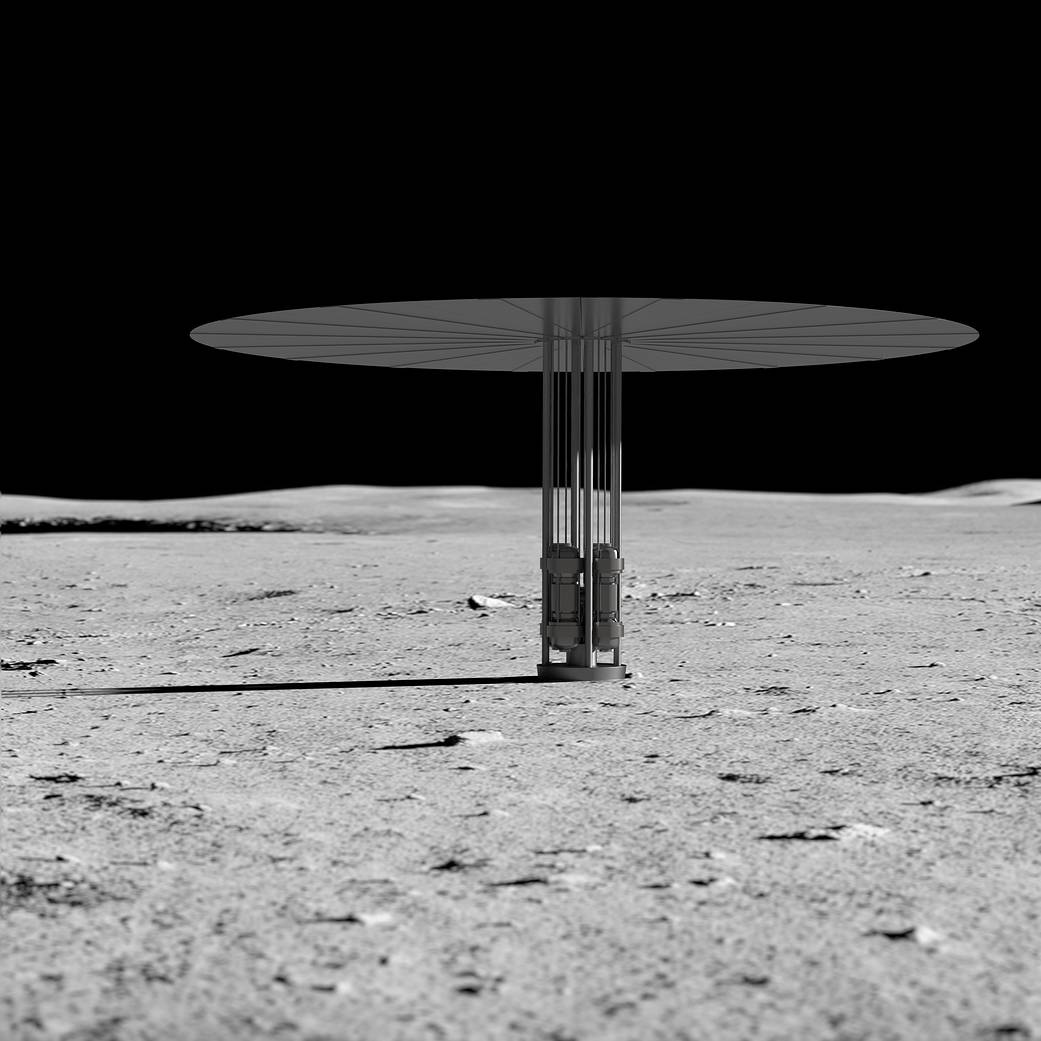

As NASA learns more about living and working on the Moon, astronauts will begin to stay for long periods. This presents a unique set of challenges in terms of available sunlight and temperatures on the surface. To help overcome these challenges, NASA is advancing a broad portfolio of surface power generation and distribution systems – like batteries, solar, and fission – that will work together to ensure those missions have plentiful, reliable power required to be successful, while also providing ideas and solutions for improving and modernizing power grids here on Earth.
NASA is developing fission surface power , a green technology with zero carbon emission. When used with advanced fuel cells, fission power can not only generate clean and abundant electricity on Earth but also provide a source of hydrogen to power zero-emission vehicles. The advances NASA makes for lunar surface power systems will help reduce the size and complexity of systems on Earth and enhance the production of smaller systems that can be used to power small communities, decreasing our dependence on large, remote power plants and energy distribution costs.
NASA has supported the development of advanced solar array systems that are lighter, more compact, and produce more energy for long-duration missions to the Moon and beyond.
Redwire’s Roll-out Solar Array (ROSA) system — developed with support from NASA — uses a lightweight flexible composite blanket material to collect a large amount of sunlight while compactly stowing for launch. When commanded to deploy, the arrays unfurl like a yoga mat and lock into position.
This innovative system was tested on the International Space Station in 2017. Recently, a more advanced version of ROSA, called iROSA, was installed on the space station, and Gateway’s Power and Propulsion Element will also use a much larger version of ROSA. This type of system could provide an easily transportable, reliable power solution for disaster response and other Earth-based applications.
Additionally, NASA will test solar cell technologies and measure solar array electrical surface charging to better understand power challenges on the Moon.
The Photovoltaic Investigation on the Lunar Surface, or PILS, experiment, will provide a flight demonstration of multiple innovative solar cell technologies that could be used for future lunar missions and perhaps applicable on Earth.
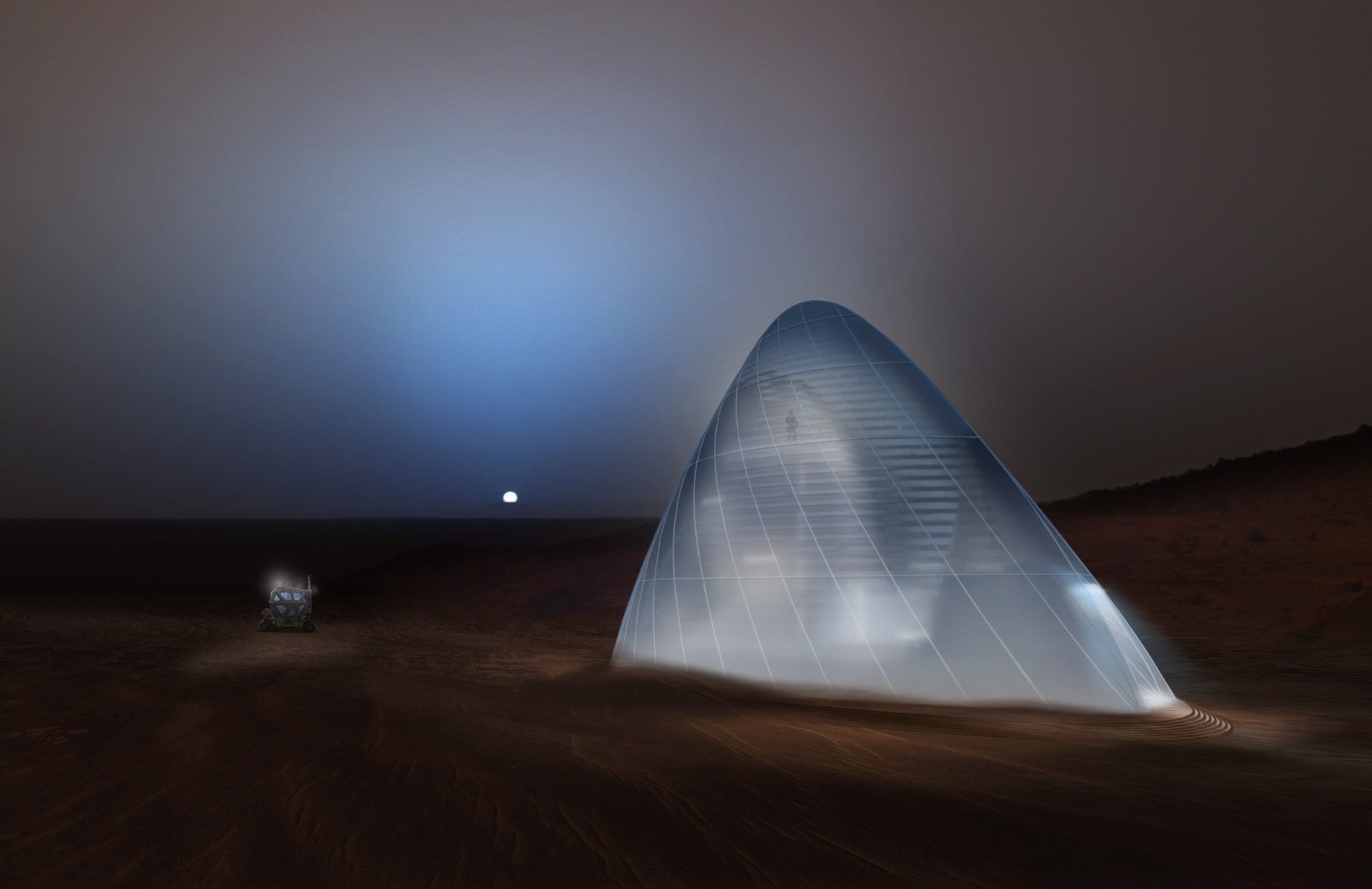

The ability to build spare parts, habitats, and other materials in-space is critical to the success of Artemis and other deep space exploration efforts. NASA has been very successful printing parts on the International Space Station and has now turned some of its efforts to manufacturing on the Moon.
In 2019, NASA awarded over $2M for solutions to the 3D Printed Habitat Challenge, a public prize competition aimed at developing a 3D-printed habitat for deep space exploration. The multi-phase challenge was designed to advance the construction technology for the Moon and Mars, but the technologies and processes can also be used to create sustainable housing solutions here on Earth.
While also related to space power, NASA is leveraging in-space printing to demonstrate a new solar technology called perovskite as alternative to silicon solar cells. The perovskite material’s use as a solar cell is a relatively new discovery, a very efficient converter of sunlight to electricity and may be transported into space as a liquid and printed onto panels while on the Moon or Mars. This solution could also have many Earth applications as well, like providing solar power to hard-to-reach areas in underdeveloped countries or during natural disaster recovery

Long-duration space explorers will need fresh food, clean air, and a reliable water source, whether during an extended stay on the Moon or a two- to- three-year round trip to Mars. The same is true for people on Earth, where climate change and population growth already cause food insecurity for many communities.
Several technologies developed for space are already making impacts here on Earth, like advancements in vertical farming and bioreactors that cultivate edible protein sources. The lessons learned are inspiring an unconventional new generation of farmers. Additionally, solutions from NASA’s Deep Space Food Challenge could enable new avenues for food production around the world, especially in extreme environments, resource-scarce regions, and in new places like urban areas and in locations where disasters disrupt critical infrastructure.
Aboard the International Space Station, NASA is advancing technologies that purify air and water to keep astronauts safe and reduce the amount of supplies that need to be delivered aboard cargo resupply ships. In the ultimate indoor environment that has housed astronauts continuously for more than 20 years, NASA has reached water recycling and purification rates of more than 90%, including condensate from the air, sweat, and urine. Air-purifying technologies aboard the space station scrub impurities from the air and even break down harmful gaseous compounds into beneficial elements like oxygen. Early in the COVID-19 pandemic, companies developing these clean air technologies were overwhelmed with demand from schools, hospitals, shopping centers, office buildings, airports, and even buses.

When Artemis astronauts return to the lunar surface, they’ll have to contend with the dust. Much like it did during Apollo, Moon dust gets into everything and is very abrasive, like tiny shards of glass, and can harm astronauts’ equipment and their health, namely their lungs.
Through a public-private partnership, NASA requested help from U.S. industry in addressing the lunar dust problem, and Lunar Outpost Inc., developed an air-quality sensor called Space Canary . The Canary-S is a self-contained, solar-powered unit that measures a variety of pollutants and provides measurements every minute via messages sent by cellular data to a secure cloud for access by company engineers and NASA. While Canary hasn’t been sent to the Moon yet, it is deployed in 15 states, and is used by the U.S. Forest Service to monitor forest-fire emissions in real-time.
Developed as a highly accurate, early fire detection system for space, the Multi-Parameter Aerosol Scattering Sensor (MPASS), has the potential to become a public safety tool for aerosol detection, with the ability to detect atmospheric particles, enabling real-time environmental monitoring during volcanic activity or wildfires. This advanced sensor uses a durable, compact laser array – like those found in a DVD player – to analyze the interaction of light with particles. It’s compact size and lightweight makes it portable and flexible for uses in multiple environments, including mounting on remotely piloted aircraft.
The technology development path is a two-way street and sometimes what is created as a concept for human space exploration is applicable today on Earth. NASA works with dozens of space agencies and thousands of companies around the world to develop innovative technologies to advance human space travel. The technical leaps and bounds since the dawn of the space age have found far-reaching applications to improve life on Earth.
Dive in to learn more about space in your life at: https://spinoff.nasa.gov/
Discover More Topics
Space Station Technology Demonstration

Latest News from Space Station Research

Biological & Physical Science Stories

Related Terms
- ISS Research
- For Researchers
- International Space Station (ISS)
- Science & Research
20 Inventions We Wouldn't Have Without Space Travel

- COP Climate Change
- Coronavirus (COVID-19)
- Cancer Research
- Diseases & Conditions
- Mental Health
- Women’s Health
- Circular Economy
- Sustainable Development
- Agriculture
- Research & Innovation
- Digital Transformation
- Publications
- Academic Articles
- Health & Social Care
- Environment
- Research & Innovation
- HR & Training
- Stakeholders
- Asia Analysis
- North America Analysis
- Our Audience
- Marketing Information Pack
- Prestige Contributors
- Testimonials

- Special Reports
- North America
- Open Access News
Space technology: how space benefits life on earth

M F Warrender highlights how space technology plays an integral role in society and how NASA invests in technology development
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), was established in 1958 by President Dwight D. Eisenhower with the vision: “we reach for new heights and reveal the unknown for the benefit of humankind.” Since then, thousands of people have been working for NASA around the world to try and achieve this.
NASA addresses a number of key questions. What’s out there in space? How do we get there? What will we find? What can we learn from space that will make life better here on Earth? Throughout history, NASA has conducted or funded research that has led to numerous improvements to life here on earth, as well as also broadened our knowledge of space.
NASA conducts its work within 4 principal organisations, called mission directorates:
- Aeronautics;
- Human exploration and operations;
- Space technology.
The latter of these mission directorates, space technology, is responsible for rapidly developing, innovating, demonstrating, and infusing revolutionary and high pay off technologies that enable NASA’s future missions, while also providing economic benefit to the nation.
NASA stands by its belief that technology drives exploration. NASA’s pioneering leadership in space is aided by sustained investments in technology, which advance the agency’s space exploration, science and aeronautics capabilities. The federal agency seeks to improve our ability to access and travel through space; land more mass in more locations throughout the solar system; live and work in deep space and on planetary bodies; build next generation air vehicles, and transform the ability to observe the universe and answer profound questions in earth and space sciences. NASA also states that its technology development supports the nation’s innovation economy by creating solutions that generate tangible benefits for life on earth. NASA is without a doubt, investing in the future of innovation and the importance of research.
Space technology and innovation
Naturally, it would be easy to assume that the many science and innovation projects generated by NASA could often overlook the impacts on other sectors, such as health and the environment. Major programmes often have large environmental impacts, with science frequently and unintentionally overlooking the importance of the preservation of the climate. However, for many years, NASA has prided itself on its attention to environmental impacts, striving to lessen the use of ozone-depleting substances and the environmental consequences of research and innovation of space technology. This has been explicitly highlighted within a statement made by former NASA administrator Dan Goldin in 1994, in which he states: “NASA must be a leader in reducing the use of ozone-depleting substances and continue to identify programme and process revisions to reduce any adverse environmental impacts.”
Since then, this notion has been maintained and reinforced through recent programmes, securing NASA’s word on its environmental consciousness. The use of solar panels to power satellites has been a constant focal point of improvement, with NASA aiming to develop traditional solar panels to make them more cost-efficient and less bulky, ensuring that solar array technology can be at its best.
Supercomputers
Another example of NASA’s environmental excellence is this year’s new modular supercomputing facility – saving energy and water. Many facilities require significant amounts of water on a day to day basis and the task of powering these facilities consumes huge amounts of energy and water, for example, heating up and cooling down a high-end computing facility. A new system has recently been developed at Ames Research Centre in Silicon Valley, named Electra, which is expected to save about 1,300,000 gallons of water and a million kilowatt-hours of energy each year, equal to the annual energy usage of about 90 households. On top of this, it will also save NASA about $35 million dollars – about half the cost of building another big facility.
Despite what might be assumed, the reduced use of water and energy resources does not lessen the system’s capability. “The Electra system will provide users an additional 280 million hours of computing time per year”, according to Bill Thigpen , Chief of the Advanced Computing Branch at Ames’ NASA Advanced Supercomputing Facility. It already ranks 39th in the US on the TOP500 list of the most powerful computer systems.
This is just one of many recent developments by NASA to help with conservation, and it just goes to show that space technology and science really can benefit other areas of society. NASA has been true to its word regarding its efforts with the environment, and as stated by Goldin, “Environmental excellence is a way of life and must be ingrained as part of our culture.
Whether it is designing and fabricating robotic spacecraft, launching the shuttle, or conducting basic research, we must seek solutions which are environmentally benign.”
M F Warrender
Open Access Government
www.openaccessgovernment.org
RELATED ARTICLES MORE FROM AUTHOR

Changing the future of prosthetic care for veterans

Exploring the gender disparity in STEM and how to change this going foward

£16 million investment to further a UK and Switzerland science partnership

Space exploration with NASA: Where will space research take us in 2025?

New Future Medicines Institute backed by £55 million funding

Japan and Horizon Europe: Negotiations began for Japan’s association
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Related Articles

Developing mathematics teacher confidence through increasing understanding of mathematics

Communicating science: The “significance” of statistics

Cell biology research: The mystery of cholesterol homeostasis
Advertisements.

Open Access Government produces compelling and informative news, publications, eBooks, and academic research articles for the public and private sector looking at health, diseases & conditions, workplace, research & innovation, digital transformation, government policy, environment, agriculture, energy, transport and more.
- Twitter (X)
Quick Links
- Our Editors
Legal & Marketing
- Terms & Conditions
- Privacy Policy
- GDPR Privacy Policy
- Marketing Info Pack
- Fee Schedule

As a Crossref Sponsored Member we are able to connect your content with a global network of online scholarly research, currently over 20,000 other organizational members from 160 countries. Crossref drive metadata exchange and support nearly 2 billion monthly API queries, facilitating global research communication.
© Adjacent Digital Politics Ltd
Language selection
- Français fr
Everyday benefits of space exploration
Some examples of how space benefits Canadians and all of humanity.

Services and information
Improving health care.
Experiments performed in space help us understand health problems on Earth.
Protecting our planet and our environment
Satellites provide data on climate change, measure pollution, and help protect our planet.
Creating scientific and technical jobs
The space sector generates high-tech jobs for Canadians.
Improving our day-to-day lives
Space technologies improve products we use every day, weather forecasts, and communications worldwide.
Enhancing safety on Earth
Satellites data can be used to predict natural disasters and to support emergency relief efforts.
Making scientific discoveries
Scientific breakthroughs are challenging our assumptions and pushing our boundaries by exploring the unknown.
Sparking youth's interest in science
Astronauts encourage young people to study science, technology, engineering and mathematics.
Cooperating with countries around the world
Canada is a partner of the International Space Station, a research laboratory in space.
- Facebook: CanadianSpaceAgency
- X: @csa_asc
- Youtube: Canadianspaceagency
- Instagram: canadianspaceagency
- Linkedin: Canadian Space Agency
- Science, Tech, Math ›
- Astronomy ›
- Space Exploration ›
Space Exploration Pays Off Here on Earth
- Space Exploration
- An Introduction to Astronomy
- Important Astronomers
- Solar System
- Stars, Planets, and Galaxies
- Weather & Climate
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/ccp_head2-58b8438e3df78c060e67b2ce.jpg)
- M.S., Journalism and Mass Communications, University of Colorado - Boulder
- B.S., Education, University of Colorado
Every so often someone asks the question, "What good does space exploration do for us here on Earth?" It's one that astronomers, astronauts, space engineers and teachers answer nearly every day.
It's simple: space exploration pays off in goods, technology, and paychecks. The work is done by people who are paid to do it here on Earth. The money they receive helps them buy food, get homes, cars, and clothing. They pay taxes in their communities, which helps keep schools going, roads paved, and other services that benefit a town or city. The money may be spent to send things "up there", but it gets spent "down here." It spreads out into the economy.
Another way to look at the "return on investment" for space exploration is that it helps pay the bills right here on the planet. Not only that but the products of space exploration range from the knowledge that gets taught to science research that benefits a wide variety of industries and technology (such as computers, medical devices, etc.) that are used here on Earth to make life better. It's really a win-win situation for everybody involved.
What are Space Exploration Spin-offs?
The products of space exploration touch lives in more ways than people think. For example, anyone who has ever had a digital x-ray, or a mammogram, or a CAT scan, or been hooked up to a heart monitor, or had specialized heart surgery to clear blockages in their veins, they've benefited from technology first built for use in space. Medicine and medical tests and procedures are HUGE beneficiaries of space exploration technology and techniques. Mammograms to detect breast cancer are another good example.
Farming techniques, food production and the creation of new medicines are also impacted by space exploration technologies. This directly benefits all of us, whether we are food producers or simply food and medicine consumers. Each year NASA (and other space agencies) share their "spinoffs", reinforcing the very real role that they play in everyday lives.
Talk to the World, Thanks to Space Exploration
Cell phones are used all over Earth. They use\ processes and materials developed for space-age communication. They "talk" to GPS satellites circling our planet, giving location data. There are other satellites monitoring the Sun that warn scientists, astronauts, and satellite owners of upcoming space weather "storms" that could affect communications infrastructure.
Users are reading this story on a computer, hooked up to a worldwide network, all made from materials and processes developed for sending science results around the world. Many people watch television using data transferred via satellites stationed in space around the world.
Entertain Yourself
Personal entertainment electronics are also a spinoff from the space age. The music people listen to on personal players is delivered as digital data: ones and zeroes, the same as any other data delivered via computers. It's also the same method that helps deliver information from weather satellites, orbiting telescopes, and spacecraft at other planets. Space exploration required the ability to transform information into data that our machines can read. Those same machines power industries, homes, education, medicine, and many other things.
Explore Distant Horizons
Travel much? The airplanes we fly in, the cars we drive, the trains we ride in and the boats we sail on all use space-age technology to navigate. Their construction is influenced by lighter materials used to build spacecraft and rockets. Although few of us are able to travel to space, our understanding of it is enlarged by the use of orbiting space telescopes and probes that explore other worlds. For example, every day or so, new images come to Earth from Mars , sent by robotic probes that deliver new views and studies for scientists to analyze. People also explore the sea bottoms of our own planet using craft influenced by the life support systems needed to survive in space.
What Does All This Cost?
There are countless examples of space exploration benefits that we could discuss. But, the next big question people ask is "How much does this cost us?"
The answer is that space exploration may cost some money up front, just as any investment does. However, it pays for itself many times over as its technologies are adopted and used here on Earth. Space exploration is a growth industry and gives good (if long-term) returns. NASA's budget for the year 2016, for example, was $19.3 billion, which will be spent here on Earth at NASA centers, on contracts to space contractors, and other companies that supply whatever it is that NASA needs. None of it is spent in space. The cost works out to a penny or two for each taxpayer. The return to each of us is much higher.
As a part of the general budget, NASA's portion is less than one percent of the total federal spending in the U.S. That's far, far less than military spending, infrastructure costs, and other expenses the government takes on. It gets us many things in our daily lives that we never connected to space, from cellphone cameras to artificial limbs, cordless tools, memory foam, smoke detectors, and much more.
For that sliver of money, NASA's "return on investment" is very good. For each dollar spent on NASA's budget, somewhere between $7.00 and $14.00 is returned back into the economy. That's based on the income from spinoff technologies, licensing, and other ways that NASA money is spent and invested. That's just in the U.S. Other countries engaged in space exploration very likely see good returns on their investments, as well as good jobs for trained workers.
Future Exploration
In the future, as humans spread out to space , the investment in space exploration technologies such as new rockets and light sails will continue to spur jobs and growth on Earth. As always, the money spent to get "out there" will be spent right here on the planet.
- The Future of Human Space Exploration
- The Story of Sputnik 1
- Neil Armstrong Quotes
- What's it Like to Live in Space?
- The History of the Chinese Space Program
- Who Was Yuri Gagarin?
- Visiting the Johnson Houston Space Center
- 16 Black Americans in Astronomy and Space
- The History of the European Space Agency
- The Best Astronomy Apps for Smartphones, Tablets, and Computers
- Biography of Robert H. Goddard, American Rocket Scientist
- Biography of Gregory Jarvis, Challenger Astronaut
- Take a Space-Themed Vacation Here on Earth
- Terrestrial Planets: Rocky Worlds Close to the Sun
- Model Rockets: A Great Way to Learn about Spaceflight
- The Evolution of the Space Suit

IMAGES
COMMENTS
5. Student research in space. People born after November 2000 have always known life with humans in space: they grew up in a world with an International Space Station orbiting overhead. Call them Generation Station, those for whom space has always seemed accessible, a place where scientists from around the globe conduct research.
The evolution of fluid physics research: Fluids cover our planet, but sending them to space can help us better understand how they flow. The study of fluids in space has progressed from fundamental research into the testing of technology applications ranging from advanced medical devices to heat transfer systems.
Let's look at how space exploration benefits our home planet. 1. Advanced Robotics and AI. Space, and everything outside of Earth's atmosphere, is a harsh environment. Robots and AI are our mechanisms of exploration, and the best minds are always at work developing the technology that allows us to roam the surface of Mars and beyond.
Learning to capture asteroids full of ice and crashing them safely, could help us solve one of the biggest challenges of inhabiting planets. The lack of liquid water. 8. Space tourism industry. The biggest dream some of us have is being able to take a trip to outer space. It is the ultimate destination.
Space exploration and its relationship with Earth is symbiotic. Often, what works for one benefits the other, and vice versa. This Earth Day, as NASA prepares to send humans farther into the solar system than ever before, the agency is advancing its understanding of fundamental sciences on the International Space Station and working on technologies for Artemis that will benefit future space ...
Space travel has given us a wealth of knowledge which has in turn helped us create inventions and technologies that have made human life easier and helped us learn more and explore further into the universe. ... JPL is a federally funded research and development center managed for NASA by Caltech.
Space research has made significantly contributions to our understanding of Earth's environment. Satellites equipped with sensors monitor climate change, track natural disasters, and help manage agricultural practices. These capabilities are essential for developing sustainable solutions to the challenges we face on Earth.
M F Warrender highlights how space technology plays an integral role in society and how NASA invests in technology development. The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), was established in 1958 by President Dwight D. Eisenhower with the vision: "we reach for new heights and reveal the unknown for the benefit of humankind." Since then, thousands of people have been working ...
Experiments performed in space help us understand health problems on Earth. Protecting our planet and our environment. Satellites provide data on climate change, measure pollution, and help protect our planet. Creating scientific and technical jobs. The space sector generates high-tech jobs for Canadians. Improving our day-to-day lives
Another way to look at the "return on investment" for space exploration is that it helps pay the bills right here on the planet. Not only that but the products of space exploration range from the knowledge that gets taught to science research that benefits a wide variety of industries and technology (such as computers, medical devices, etc.) that are used here on Earth to make life better.