- To save this word, you'll need to log in. Log In
problem-solving

Definition of problem-solving
Examples of problem-solving in a sentence, dictionary entries near problem-solving, cite this entry.
“Problem-solving.” Merriam-Webster.com Dictionary , Merriam-Webster, https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/problem-solving. Accessed 20 Dec. 2024.
Subscribe to America's largest dictionary and get thousands more definitions and advanced search—ad free!

Can you solve 4 words at once?
Word of the day.
See Definitions and Examples »
Get Word of the Day daily email!
Popular in Grammar & Usage
Point of view: it's personal, plural and possessive names: a guide, what's the difference between 'fascism' and 'socialism', more commonly misspelled words, words you always have to look up, popular in wordplay, 8 words with fascinating histories, 8 words for lesser-known musical instruments, birds say the darndest things, 10 words from taylor swift songs (merriam's version), 10 scrabble words without any vowels, games & quizzes.

- Cambridge Dictionary +Plus
Meaning of problem-solving in English
Your browser doesn't support HTML5 audio
- problem-solver
Examples of problem-solving

Word of the Day
a turn made by a car in order to go back in the direction from which it has come

It’s written in the stars: talking about things that might happen in the future

Learn more with +Plus
- Recent and Recommended {{#preferredDictionaries}} {{name}} {{/preferredDictionaries}}
- Definitions Clear explanations of natural written and spoken English English Learner’s Dictionary Essential British English Essential American English
- Grammar and thesaurus Usage explanations of natural written and spoken English Grammar Thesaurus
- Pronunciation British and American pronunciations with audio English Pronunciation
- English–Chinese (Simplified) Chinese (Simplified)–English
- English–Chinese (Traditional) Chinese (Traditional)–English
- English–Dutch Dutch–English
- English–French French–English
- English–German German–English
- English–Indonesian Indonesian–English
- English–Italian Italian–English
- English–Japanese Japanese–English
- English–Norwegian Norwegian–English
- English–Polish Polish–English
- English–Portuguese Portuguese–English
- English–Spanish Spanish–English
- English–Swedish Swedish–English
- Dictionary +Plus Word Lists
- problem-solving
- All translations
To add problem-solving to a word list please sign up or log in.
Add problem-solving to one of your lists below, or create a new one.
{{message}}
Something went wrong.
There was a problem sending your report.
- Privacy Policy
Educational Psyche
Inductive To Innovative
Problem Solving Method and Detailed Explanation of 7 Steps
What is a Problem-Solving Method?
First, let’s understand the term “problem-solving.” When we encounter difficulties in doing something, we identify the problem, analyze its root causes, and then attempt to find a solution. This entire process is known as problem-solving. We often engage in this process in our daily lives, as we all face challenges while trying to accomplish tasks.
Table of Contents
Definitions
D’Zurilla and Goldfried (1971) define problem solving as “a behavioral process, whether overt or covert in nature, which (a) makes available a variety of potentially effective response alternatives for dealing with the problematic situation and (b) increases the probability of selecting the most effective response from among these various alternatives.
Who gave this method?
There is often confusion regarding the origins of this method; specifically, whether it was introduced by John Dewey or George Polya. The problem-solving method was first introduced by well respected John Dewey in the context of teaching, while George Polya contributed to it from a psychological perspective.
John Dewey (October 20, 1859 – June 1, 1952) was an American philosopher , psychologist , and educational reformer . John Dewey was the most significant educational thinker of his era and, many would argue, of the 20th century. As a philosopher, social reformer, and educator, he changed fundamental approaches to teaching and learning. His ideas about education sprang from a philosophy of pragmatism and were central to the Progressive Movement in schooling. In light of his importance, it is ironic that many of his theories have been relatively poorly understood and haphazardly applied over the past hundred years. [1] John Dewey and Jean Piaget both believed in self-regulation in intellectual thinking.
Steps of the Problem-Solving Method By John Dewey
John dewey approved seven steps in his problem-solving method:.

- Define the Problem: In this step, we aim to understand and define the exact nature of the problem. We would inform the students about the broken glass and explain the situation.
- Collect Information: We gather all relevant information related to the problem. For instance, we might find pieces of shattered glass on the floor or identify any suspicious objects nearby.
- Formulate Hypotheses: After reviewing all the information and connecting the dots, we generate thought-provoking hypotheses about potential causes and solutions. These hypotheses are essentially educated guesses regarding why the problem occurred. The teacher and students will discuss possible explanations, such as wind, someone throwing a stone, or an attempt to enter through the window.
- Test the Hypotheses: In this step, we evaluate each hypothesis one by one to determine which is most reliable. The teacher will discuss each potential cause suggested by the students and check its validity. For example, if yesterday’s weather was clear, then wind is unlikely to be a factor. If someone threw a stone, there should be evidence of it in the classroom, but if there is no stone present, that hypothesis may be dismissed.
- Construct a Physical Model: Next, we physically examine our hypotheses rather than just considering them abstractly. Creating a physical representation allows for more realistic and accurate results. The teacher and students can simulate a scenario where someone attempts to enter through the window.
- Verification of Results: After constructing the physical model, we verify whether our conclusions are correct or if we need to revisit our ideas. If the model demonstrates that it is indeed possible for someone to enter through the window, then the group may decide to install iron grills on the window to prevent future incidents.
Problem Solving Method By George Polya
George Polya was a Hungarian-American mathematician. He received his Ph.D. in mathematics at the University of Budapest. He was a professor of mathematics from 1914 to 1940 at ETH Zürich and from 1940 to 1953 at Stanford University .
George Polya became famous after his book “ How to Solve It “, in which he describe problem solving method and this method is different from Jhon Dwey’s method and views.
George Polya outlines four essential steps for effective Problem Solving:
- Understand the Problem: In this initial step, it is crucial to grasp the nature of the problem so that we can identify its possible causes and solutions. Students should read the problem carefully, analyze it, and explore its meaning. As a teacher, you can enhance this process by facilitating group discussions in a secure and friendly environment. Be available to assist students who encounter difficulties, guiding them to a clearer understanding of the situation or problem.

- Try: Now it’s time to test the proposed solutions. Check if the identified causes align with the problem and try each solution one by one. This process will help students find the most accurate solution while building their confidence in their reasoning. Encourage them to visualize their tests through charts, pictures, or other visual aids so that all students can see the outcomes and provide feedback on their thinking. Give them the opportunity to analyze their solutions independently, which will help them gain the ability to discuss their work with confidence.
- Revisit the Solution: In the final step, students evaluate their strategies after arriving at a solution. They should document the actual sequence of their problem-solving method and assess what was necessary and what could be omitted. This reflection allows them to learn from any mistakes made during the process. Provide students with the chance to analyze their work, enabling them to reflect on their learning, skills, abilities, and areas for improvement.
What is the importance of Problem Solving?
- Essential Skill: Problem solving is crucial in daily life, helping us navigate challenges and avoid feeling stuck.
- Development in Students: It’s important for students to cultivate problem-solving skills to manage obstacles and prevent overwhelm.
- Life Stages: We face various problems throughout life—school, college, work, marriage, and parenting—making regular practice essential.
- Enhances Time Management: A systematic approach to problem solving leads to accurate results more efficiently, reducing trial and error.
- Fosters Critical Thinking: It encourages analysis of situations and consideration of abstract possibilities, even when direct solutions aren’t clear.
- Avoids Risks: Strong problem-solving skills help prevent impulsive decisions that could lead to unnecessary risks.
- Facilitates Personal Growth: It ensures we don’t remain stagnant in challenging situations, promoting continuous development.
- Tracks Progress: Problem solving allows us to assess our journey, helping us determine if we’re on the right path or need to adjust our approach.
Enhancing Problem-Solving Effectiveness in the Classroom
- Connect with Real-Life Problems: Start by identifying problems relevant to students’ lives. This connection will engage them and make the problem more effective.
- Define the Problem at an Appropriate Level: Clearly explain the problem in a way that is suitable for the student’s understanding. If the explanation is unclear, students may lose interest, leading to less fruitful results.
- Encourage Hypothesis Generation: Foster an environment where students feel comfortable brainstorming multiple hypotheses. Encourage them to think creatively and explore various possibilities.
- Embrace All Ideas: Avoid discouraging students from sharing their thoughts, even if they seem unconventional. Every idea can contribute to the discussion and may lead to valuable insights.
- Involve Everyone: Ensure that all students have the opportunity to participate. This inclusivity helps everyone feel secure and valued within the classroom community.
- Practice Regularly: Use this problem-solving technique frequently in class. Regular practice will help students apply these skills in real-life situations, reinforcing their learning and confidence.
Merits of Problem Solving:
- It helps students build confidence.
- By learning this skill, individuals can solve their problems in life easily and effectively.
- It enables us to address issues without making silly mistakes.
- It provides an understanding of the entire problem-solving process.
- It fosters abstract thinking.
- Group discussions promote cooperation and collaboration among students.
- It encourages critical thinking and allows for brainstorming, which is an essential skill.
- It is a child-centered method, especially when teachers empower children and ensure that each student has the opportunity to participate.
Demerits of Problem Solving method
- It is a time-consuming method that requires proper time allocation, which may not be feasible in a classroom with a fixed syllabus.
- Teachers need to be adequately prepared for this method; however, many educators are already burdened and may not be fully prepared.
- At times, teachers may dominate the process, turning it into a teacher-centered approach rather than a student-centered one.
- This method requires teacher training; if educators are not trained and lack familiarity with the approach, student engagement may suffer.
- Group discussions can create noise and disrupt the classroom environment.
- Completing the syllabus can be challenging while using this particular method, as it demands patience and time which are often in short supply.
- Occasionally, discussions may not lead to a solution, leaving problems unresolved and potentially discouraging students.
Discover more from Educational Psyche
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
Type your email…
By Dr. Dev Arora
Hey there! I'm Dev, and let me tell you a bit about myself. Education has been my passion since I was a kid, and I've dedicated my life to teaching and learning.
Related Post
4 elements of creativity: boost your creative thinking |, 4 learning curves and plateaus by ebbinghaus: for better learning, sigmund freud & psycho analytical theory of personality : 3 dynamic ego, id, super ego, leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Notify me of follow-up comments by email.
Notify me of new posts by email.
Unlock Group Psychology: 10 ways to boost your teaching
Children with hearing and visual impairment: unlock 10 ways to foster learning, perception: 7 steps of perception & educational guidance for best learning, discover methods of personality measurement: 3 meths objective, subjective, projective for fruitful assessment.

What is Problem Solving? (Steps, Techniques, Examples)
By Status.net Editorial Team on May 7, 2023 — 4 minutes to read
What Is Problem Solving?
Definition and importance.
Problem solving is the process of finding solutions to obstacles or challenges you encounter in your life or work. It is a skill that allows you to tackle complex situations, adapt to changes, and overcome difficulties with ease.
Problem-Solving Steps
The problem-solving process typically includes the following steps:
- Identify the issue : Recognize the problem that needs to be solved.
- Analyze the situation : Examine the issue in depth, gather all relevant information, and consider any limitations or constraints that may be present.
- Generate potential solutions : Brainstorm a list of possible solutions to the issue, without immediately judging or evaluating them.
- Evaluate options : Weigh the pros and cons of each potential solution, considering factors such as feasibility, effectiveness, and potential risks.
- Select the best solution : Choose the option that best addresses the problem and aligns with your objectives.
- Implement the solution : Put the selected solution into action and monitor the results to ensure it resolves the issue.
- Review and learn : Reflect on the problem-solving process, identify any improvements or adjustments that can be made, and apply these learnings to future situations.
Defining the Problem
To start tackling a problem, first, identify and understand it. Analyzing the issue thoroughly helps to clarify its scope and nature. Ask questions to gather information and consider the problem from various angles. Some strategies to define the problem include:
- Brainstorming with others
- Asking the 5 Ws and 1 H (Who, What, When, Where, Why, and How)
- Analyzing cause and effect
- Creating a problem statement
Generating Solutions
Once the problem is clearly understood, brainstorm possible solutions. Think creatively and keep an open mind, as well as considering lessons from past experiences. Consider:
- Creating a list of potential ideas to solve the problem
- Grouping and categorizing similar solutions
- Prioritizing potential solutions based on feasibility, cost, and resources required
- Involving others to share diverse opinions and inputs
Evaluating and Selecting Solutions
Evaluate each potential solution, weighing its pros and cons. To facilitate decision-making, use techniques such as:
- SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats)
- Decision-making matrices
- Pros and cons lists
- Risk assessments
After evaluating, choose the most suitable solution based on effectiveness, cost, and time constraints.
Implementing and Monitoring the Solution
Implement the chosen solution and monitor its progress. Key actions include:
- Communicating the solution to relevant parties
- Setting timelines and milestones
- Assigning tasks and responsibilities
- Monitoring the solution and making adjustments as necessary
- Evaluating the effectiveness of the solution after implementation
Utilize feedback from stakeholders and consider potential improvements.
Problem-Solving Techniques
During each step, you may find it helpful to utilize various problem-solving techniques, such as:
- Brainstorming : A free-flowing, open-minded session where ideas are generated and listed without judgment, to encourage creativity and innovative thinking.
- Root cause analysis : A method that explores the underlying causes of a problem to find the most effective solution rather than addressing superficial symptoms.
- SWOT analysis : A tool used to evaluate the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats related to a problem or decision, providing a comprehensive view of the situation.
- Mind mapping : A visual technique that uses diagrams to organize and connect ideas, helping to identify patterns, relationships, and possible solutions.
Brainstorming
When facing a problem, start by conducting a brainstorming session. Gather your team and encourage an open discussion where everyone contributes ideas, no matter how outlandish they may seem. This helps you:
- Generate a diverse range of solutions
- Encourage all team members to participate
When brainstorming:
- Reserve judgment until the session is over
- Encourage wild ideas
- Combine and improve upon ideas
Root Cause Analysis
For effective problem-solving, identifying the root cause of the issue at hand is crucial. Try these methods:
- 5 Whys : Ask “why” five times to get to the underlying cause.
- Fishbone Diagram : Create a diagram representing the problem and break it down into categories of potential causes.
- Pareto Analysis : Determine the few most significant causes underlying the majority of problems.
SWOT Analysis
SWOT analysis helps you examine the Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats related to your problem. To perform a SWOT analysis:
- List your problem’s strengths, such as relevant resources or strong partnerships.
- Identify its weaknesses, such as knowledge gaps or limited resources.
- Explore opportunities, like trends or new technologies, that could help solve the problem.
- Recognize potential threats, like competition or regulatory barriers.
SWOT analysis aids in understanding the internal and external factors affecting the problem, which can help guide your solution.

Mind Mapping
A mind map is a visual representation of your problem and potential solutions. It enables you to organize information in a structured and intuitive manner. To create a mind map:
- Write the problem in the center of a blank page.
- Draw branches from the central problem to related sub-problems or contributing factors.
- Add more branches to represent potential solutions or further ideas.
Mind mapping allows you to visually see connections between ideas and promotes creativity in problem-solving.
- Problem Solving Skills: 25 Performance Review Phrases Examples
- How to Resolve Employee Conflict at Work [Steps, Tips, Examples]
- 30 Examples: Self Evaluation Comments for Problem Solving
- Effective Decision Making Process: 7 Steps with Examples
- 174 Performance Feedback Examples (Reliability, Integrity, Problem Solving)
- How to Write Inspiring Core Values? 5 Steps with Examples
- Onsite training
3,000,000+ delegates
15,000+ clients
1,000+ locations
- KnowledgePass
- Log a ticket
01344203999 Available 24/7

What is Problem Solving? A Comprehensive Guide
In this blog, we will explore "What is Problem Solving?" In detail. From defining the nature of Problem Solving to understanding the key process in resolving issues, this blog covers it all. So, wait no more; let’s go deeper into this fundamental concept.

Exclusive 40% OFF
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Share this Resource
- Introduction to Management
- Personal & Organisational Development
- Workforce Resource Planning Training
- Supervisor Training
- Introduction to Managing Budgets

Table of contents
1) What is Problem Solving definition?
2) The process of Problem Solving
3) Key skills for effective Problem Solving
4) Strategies for enhancing Problem Solving abilities
5) Problem Solving tools and techniques
6) Conclusion
What is Problem Solving definition?

The process of Problem Solving
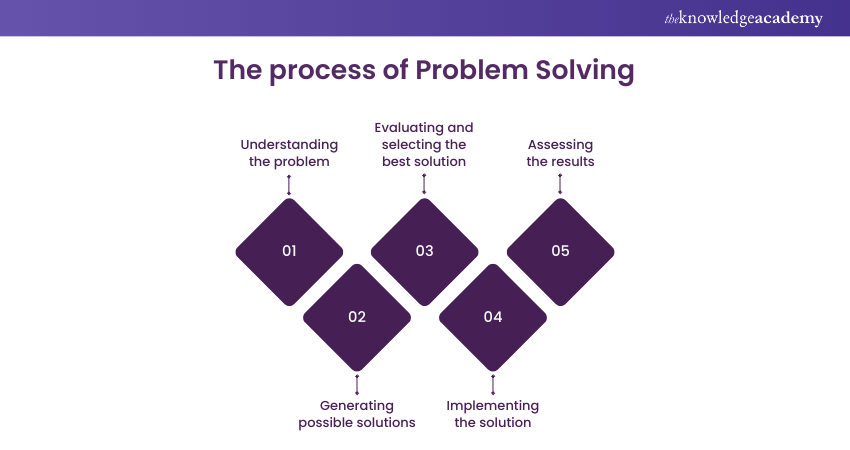
Understanding the problem
The first step in Problem Solving is gaining a clear understanding of the issue at hand. Take the time to thoroughly analyse the problem and gather relevant information. Ask yourself questions like:
1) What is the nature of the problem?
2) What are the factors contributing to the problem?
3) What are the desired outcomes?
4) Are there any constraints or limitations to consider?
By gaining a comprehensive understanding of the problem, you lay a solid foundation for finding an effective solution.
Generating possible solutions
Once you have a clear grasp of the problem, it's time to brainstorm potential solutions. Encourage creativity and think outside the box. Consider all possible options without judgment or criticism. The goal at this stage is to generate a variety of ideas and alternatives.
Evaluating and selecting the best solution
After generating a list of possible solutions, it's important to evaluate each option based on its feasibility, effectiveness, and alignment with the desired outcome. Consider the advantages and disadvantages of each and every solution. Assess its practicality and the resources required for implementation.
Additionally, take into account the potential risks and benefits associated with each solution. Consider any potential consequences or impacts on other aspects. Based on this evaluation, select the solution that appears most viable and promising.
Implementing the solution
Once you have chosen the best solution, it's time to put it into action. Develop a detailed plan outlining the necessary steps and allocate the required resources. Determine responsibilities and deadlines to ensure a smooth implementation process.
During implementation, monitor progress and make any necessary adjustments or adaptations. Stay proactive and address any challenges or obstacles that may arise along the way. Effective communication and collaboration with others involved in the process can greatly contribute to successful implementation.
Assessing the results
After implementing the solution, it's essential to assess the results. Evaluate whether the problem has been properly resolved or if further adjustments are required. Analyse the outcomes and compare them against the desired goals and expectations.
Consider whether the chosen solution has brought about the intended benefits and if any unexpected consequences have emerged. Reflect on the overall effectiveness of the Problem Solving process and identify any lessons learned for future reference.
Remember, Problem Solving is an iterative process, and it's not uncommon to revisit and refine solutions based on ongoing evaluation and feedback. Embrace a continuous improvement mindset and be open to seeking alternative approaches if necessary.
By following this Problem Solving process, you can approach challenges systematically and increase your chances of finding effective solutions. Remember that practice and experience play a vital role in honing your skills.
Master the art of solving problems and become a catalyst for innovation and success with our Problem Solving Training – sign up now!
Key skills for effective Problem Solving
What one must do to become an effective problem solver is to develop key skills that enhance your Problem Solving abilities. The skills give you the ability to tackle challenges with a strategic mind and find the needed solutions. Below is a dive into the most important of them:
Critical thinking
Critical thinking is a skill that includes the objective analysis of information, considering different viewpoints, and being able to arrive at a sensible judgment. This helps you to assess problems with the right accuracy in judgment and also find suitable solutions.
It means that creativity is the ability of a person to think outside the box and come up with innovative solutions. It includes pressing the mind toward new possibilities and viewing the problem in different ways.
Analytical skills
In this ability, there is the aspect of breaking down a problem into subunits that helps in identifying the patterns, relationships, and causes within the problem.
Decision-making
Sound skills in decision making call for the assessment of the pros and cons of all solutions provided and thus choosing the best alternative. Risks must always be considered with the benefits any alternative might bring.
Strategies for enhancing Problem Solving abilities
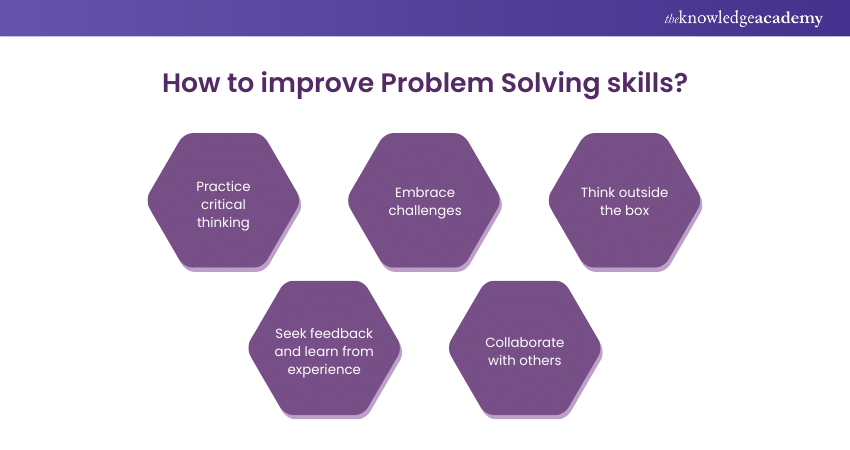
Practice critical thinking
Engage yourself in activities which require critical thinking, including solving puzzles, complex discussion, challenging all assumptions. This will increase your ability to enhance sharpening of your analytical skills and let you think critically at a time when problems are in your way.
Seek feedback and learn from experience
Seek responses from your mentors, course peers, and Problem Solving experts. From the successes and failures, reflect on the reasons for the occurrences over previous experiences and point out what could be improved. Treat the opportunity of Problem Solving as one of the chances that shall be given to you to grow and develop each time you make it through a problem.
Embrace challenges
You can redesign your problematic issues and take every challenge coming across as an opportunity for growth. Hence, it paves the way for the ability of resilience and strengthens your Problem Solving abilities.
Collaborate with others
In Problem Solving, collaboration is embraced by pooling different perspectives and ideas. Work with others in activities that involve groups to discuss issues and seek input from others, listening actively to various viewpoints. Working collaboratively with others helps expand your knowledge of various ways of Problem Solving and encourages innovation.
Think outside the box
Encourage creative thinking by exploring unconventional ideas and solutions. Challenge every assumption and all its related alternatives. Shift to this kind of mindset, and it can drive innovative Problem Solving strategies, letting you uncover newer ways to solve age-old complex problems.
Problem Solving tools and techniques
When faced with complex problems, utilising specific tools and techniques can help facilitate the solving process and lead to more effective solutions. Here are some commonly used Problem Solving tools and techniques:
Root cause analysis
Root cause analysis is a methodology used to detect the underlying causes of a problem. It involves investigating the problem's symptoms and tracing them back to their fundamental causes. By addressing the root causes, Problem Solvers can prevent the issue from recurring.
Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats (SWOT) analysis
SWOT analysis is a planning tool that strategically helps measure the weaknesses and internal strengths of a situation. Moreover, it can find external opportunities and threats. By assessing these factors, Problem Solvers can gain insights into the current state and make informed decisions about potential solutions.
Fishbone diagrams
Fishbone diagrams, also known as cause-and-effect diagrams or Ishikawa Diagrams, visually represent the possible causes contributing to a problem. By organising causes into categories (such as people, process, equipment, and environment), Problem Solvers can systematically analyse the problem's potential sources.
Decision matrices
Decision matrices are used to evaluate and compare different options based on multiple criteria. This tool helps Problem Solvers weigh the importance of various factors and objectively assess each alternative, leading to an informed decision.
Six Thinking Hats
Six Thinking Hats is a technique initially developed by Edward de Bono that encourages parallel thinking by exploring different perspectives. Each "hat" represents a different thinking approach (e.g., logical, creative, emotional), allowing Problem Solvers to consider diverse viewpoints and generate innovative solutions.
These are just a few examples of Problem Solving tools and techniques. Depending on the nature of the problem, other methods, such as brainstorming, mind mapping, flowcharts, or Pareto analysis, can also be applied. Choosing the appropriate tool or technique depends on the specific problem and the desired outcome.
Navigate conflicts with finesse and foster collaboration with our transformative Conflict Management Training – sign up today!
Conclusion
We hope you read and understand everything about What is Problem Solving? Developing effective skills is crucial for overcoming challenges, making informed decisions, and achieving success. By embracing problems as opportunities and applying strategic approaches, individuals can become proficient Problem Solvers in various domains of life.
Unlock your management potential and elevate your skills to new heights with our cutting-edge Management Courses – sign up now!
Frequently Asked Questions
There are two major types of Problem Solving: Reflective and Creative. Regardless of the type, it focuses on understanding the issues, considering all factors and finding a solution.
Problem Solving in the workplace refers to an individual’s ability to manage difficult situations and find solutions to complex business issues.
The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs , videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA .
The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass , a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.
The Knowledge Academy offers various Management Courses including Business Process Improvement Training, Performance Management Training and Introduction to Managing People. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Resource Planning Template .
Our Business Skills Blogs cover a range of topics related to musical instruments, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your skills as a Music Producer, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have you covered.
Upcoming Business Skills Resources Batches & Dates
Fri 21st Feb 2025
Fri 25th Apr 2025
Fri 20th Jun 2025
Fri 22nd Aug 2025
Fri 17th Oct 2025
Fri 19th Dec 2025
Get A Quote
WHO WILL BE FUNDING THE COURSE?
My employer
By submitting your details you agree to be contacted in order to respond to your enquiry
- Business Analysis
- Lean Six Sigma Certification
Share this course
Biggest christmas sale.

We cannot process your enquiry without contacting you, please tick to confirm your consent to us for contacting you about your enquiry.
By submitting your details you agree to be contacted in order to respond to your enquiry.
We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Or select from our popular topics
- ITIL® Certification
- Scrum Certification
- ISO 9001 Certification
- Change Management Certification
- Microsoft Azure Certification
- Microsoft Excel Courses
- Explore more courses
Press esc to close
Fill out your contact details below and our training experts will be in touch.
Fill out your contact details below
Thank you for your enquiry!
One of our training experts will be in touch shortly to go over your training requirements.
Back to Course Information
Fill out your contact details below so we can get in touch with you regarding your training requirements.
* WHO WILL BE FUNDING THE COURSE?
Preferred Contact Method
No preference
Back to course information
Fill out your training details below
Fill out your training details below so we have a better idea of what your training requirements are.
HOW MANY DELEGATES NEED TRAINING?
HOW DO YOU WANT THE COURSE DELIVERED?
Online Instructor-led
Online Self-paced
WHEN WOULD YOU LIKE TO TAKE THIS COURSE?
Next 2 - 4 months
WHAT IS YOUR REASON FOR ENQUIRING?
Looking for some information
Looking for a discount
I want to book but have questions
One of our training experts will be in touch shortly to go overy your training requirements.
Your privacy & cookies!
Like many websites we use cookies. We care about your data and experience, so to give you the best possible experience using our site, we store a very limited amount of your data. Continuing to use this site or clicking “Accept & close” means that you agree to our use of cookies. Learn more about our privacy policy and cookie policy cookie policy .
We use cookies that are essential for our site to work. Please visit our cookie policy for more information. To accept all cookies click 'Accept & close'.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Dec 5, 2016 · The meaning of PROBLEM-SOLVING is the process or act of finding a solution to a problem. How to use problem-solving in a sentence.
The term problem solving has a slightly different meaning depending on the discipline. For instance, it is a mental process in psychology and a computerized process in computer science . There are two different types of problems: ill-defined and well-defined; different approaches are used for each.
PROBLEM-SOLVING definition: the process of finding solutions to problems: . Learn more.
The A3 report is a problem-solving method that is used widely in lean to define or clarify problems, suggest solutions, and document the results of improvement activities. The thought behind the A3 report is to include all relevant information and establish a clear representation of the current problem, eliminating "waste" in the form of ...
PROBLEM-SOLVING meaning: the process of finding solutions to problems: . Learn more.
Sep 17, 2024 · Definitions. D’Zurilla and Goldfried (1971) define problem solving as “a behavioral process, whether overt or covert in nature, which (a) makes available a variety of potentially effective response alternatives for dealing with the problematic situation and (b) increases the probability of selecting the most effective response from among these various alternatives.
What Is Problem Solving? Definition and Importance Problem solving is the process of finding solutions to obstacles or challenges you encounter in your life or work. It is a skill that allows you to tackle complex situations, adapt to changes, and overcome difficulties with ease. Problem-Solving Steps The problem-solving process typically includes the following steps:...
Jul 31, 2023 · In this blog, you will learn What is Problem Solving , its process, key skills and strategies, and tools and techniques to do so. Table of contents . 1) What is Problem Solving definition? 2) The process of Problem Solving . 3) Key skills for effective Problem Solving . 4) Strategies for enhancing Problem Solving abilities
This process is a crucial part of problem-solving as being able to define the problem has been identified as one of the eight steps towards coming up with a solution (D'Zurilla & Goldfried, 1971). When you see a problem accurately, it is easier to come up with the appropriate response.
The word "problem" comes from a Greek word meaning an "obstacle" (something that is in your way). If someone has a problem, they have to find a way of solving the problem. The way to solve it is called a solution. Some problem-solving techniques have been developed and used in artificial intelligence, computer science, engineering, and ...